5) Artificial Intelligence (AI) based Smart Agriculture for Sustainable Development :
Organized by
Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Indian Statistical Institute during February 26-28, 2021
 |
| Specially A.I. Controlled Agri Drones Use for Sparying Pesticides,Water,Nutrients to Crops |
Sustainable agriculture helps find a balance between the volume of food production and proper maintenance of the ecosystem. It also promotes the economic stability of the farmers while agriculture continues to be the largest source of earning of the world population, with nearly 40% of its population relying on agriculture for their hand to mouth. Increased practice of sustainable agriculture is capable of meeting our food and textile needs, without compromising the needs of the current or future generations through the preservation of the ecosystem. This style of farming aims to produce food without the rampant use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers.
 |
| A.I. Application in the Field of Agriculture |
Artificial Intelligence based technologies have already started to shape agricultural practices in India. Some of the Indian farmers having a large volume of cultivable lands are now getting inclined to adopt smart farming strategies powered by AI enabled sophisticated technologies, autonomous tractors fitted with GPS and various other sensors including digital cameras to plant crops, apply fertilizers, spray pesticides, manage the weeds, determine the need for irrigation, predict the yield etc. in more efficient ways than ever before. ICRISAT headquartered in Hyderabad, India, is collaborating with the software giant Microsoft to enable Indian farmers to harness the power of AI to increase agricultural yields while maintaining environmental sustainability. Tech giant IBM is now providing Indian farmers and its agritech startups the opportunity to use its weather monitoring tools developed by its subsidiary, The Weather Company, free-of-cost to support smallholders and supply chain-focused startups with decision-making. In the near future, there may not be enough people to put their labour towards harvesting the required enormous volume of food and a robotic solution may hold the key to a sustainable food future that will benefit both the producers and its consumers. Harvest CROO Robotics established a few years back has developed a robot that helps farmers to pick and pack their crops. On the other hand, PEAT, a Berlin-based agricultural tech farm has developed a deep learning based application, called Plantix which is capable of detecting potential defects and nutrient deficiencies in the soil in some efficient way.
 |
| Artificial-intelligence-in-Asian-agriculture-image |
According to the World Health Organization (15th July 2019) about 820 million people did not have enough to eat in 2018, which was 811 million in the previous year, this makes it the third year of increase in a row. The second Goal of UNDP is “No Hunger” and some of the targets set under this goal are: by 2030, double the agricultural productivity and income of small-scale food producers, ensure sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agricultural practices that increase productivity and production, that help maintain ecosystems, that strengthen capacity for adaptation to climate change, extreme weather, drought, flood and other disasters and that progressively improve land and soil quality. And here comes the importance of AI assisted sustainable smart agriculture. Data-driven approaches integrating AI and machine learning with big data technologies and high-performance computing could drive agricultural productivity while minimising its environmental impact. Keeping this in mind the workshop will focus on the relevance of AI assisted smart Agriculture, tools and techniques needed for that. The workshop will discuss some of the advanced applications of AI in agriculture. It will also emphasize on how an agricultural ecosystem can be developed so that the benefits of AI can reach small farmers.
6) AI Technology In
Military Will Transform Future Warfare:
 |
| A.I. Controlled Air Drones,Unmanned Vehicles Tanks &future Robot Soldier |
TINY SWARMS OF DRONES: in the sky can rain down disaster of an unprecedented magnitude. Controlled faraway from the conventional battle field, these swarms can swoop down over territory, across international boundaries and unleash destruction powered by a barrage of cross-spectrum ammution. Threats of uninhibited intensity – without an actual declaration of war – are what militaries across the world could be left grappling with. The recent drones attack at the IAF base in Jammu is perhaps, just the beginning of this covert form of warfare.
To challenge the supremacy of the United States and for
overall development of military-AI technologies, Chinese policymakers released
their 10th defence white paper, China’s National Defense in the New Era
Roadmap, outlining the complete AI-ecosystem for the Chinese Army.
The integration of AI with regular military operations
could upgrade logistics, administration, maintenance, training, personal
management and even routine activities or exercises. It could reduce
institutional workload and free up warriors to focus on core functions.
Artificial intelligence could handle the OODA (Observe-Orient-Decide-Act) loop
faster, create combat intelligent clouds with secure gateways as well as upgrade
Command-and-Control capabilities of the armed forces with the establishment of
a resilient data-oriented highly automated approach. The Military-AI-Ecosystem
could support higher formations to design and deploy more effective and
efficient battle plans for better control of operations through sharper and
deep insights.
The new intelligent technologies could speed up decision
making capabilities which would help military leaders to take a higher number
of offensive or defensive decisions during wars or combat with greater
efficacy. Artificial intelligence will accelerate establishment of a dynamic
autonomous system for 360 degree analysis of the environment for better
real-time battlefield decision making.
Artificial intelligence has the potential to enchance
future combat skills of the military through the following:
-%20Using%20artificial%20intelligence%20(AI)%20for%20warfare%20has%20been%20the%20promise%20of%20science%20fiction%20and%20politicians%20for%20years,.jpg) |
| TEHRAN (ANA)- Using artificial intelligence (AI) for warfare has been the promise of science fiction and politicians for years, |
lAI-based smart logistics with integrated actions
lAI-based transportation system for each node of the
establishment
lAI- Enabled target recognition capabilities across
naval, air and land attack systems
lUnmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle
lUnmanned Intelligent Ground Vehicle
lAI-enabled deep analysis of integrated warfare theatres
(land, naval and air)
l Cybersecurity
l Cyber warfare
l Robotic battlefields
l Advanced war simulators
l AI-based war games for training of the forces
l Predictive & sequential analysis of threats and
situations
l Use of AI techniques for military data processing &
analysis
l AI based guided and loitering missile systems
lAI-based autonomous weapon systems.
 |
| Gladiator Tactical Unmanned Ground Vehicle at Redstone Arsena |
In modern warfare extensive strategic intelligence is
required with more sophisticated integration of technological components to
deal with the situational requirements of war theatres. War zones are one of
the areas where each discrete event is overloaded with a high volume of
unstructured unstructured data. Artificial intelligence could create taxonomies
of events from available data sets for integration and structuring of data,
thus aiding real-time decision support. As wars become driven by information,
AI can provide or recommend valuable options to the commanders that the human
brain may not be able to assess on account of the volume or decision time
stress. Global military powers are smartly working towards modelling a common
platform to handle the context-based challenges from the sea floor to space,
using convergence of disruptive technologies, combined with different tools
enabled by AI.
 |
| Artist`s Imagination about future AI based Robot Soldier |
This entire processing is making wars knowledge-based as
opposed to traditionally quantity driven – a radical shift from attrition and
destruction-based approaches to one based on effects and outcomes. The fusion
of old war skills with AI technology is driving the evolution of a new
doctrinal concept of war that is based on rapid and accurate decisions,
deployments and destruction of the adversary’s ability and will to fight –
instead of one based merely on the targeting of enemy armament and arsenal.
Physical bravery on the battlefield as we know it, has
now an additional dimension of courage in cyberspace, with the advent of
digitized warfare Artificial
intelligence is the next generation weapon required to transform the way in
which armed forces operate, train and fight – right from the barracks to the
trenches. Models based on AI are necessary for each country to demystify and
structurally address hidden war behaviours of the enemy. Accurate decisions
supported by AI could create an exponential impact on the conduct and outcome
of wars. Another dimension to this is the possibility of tweaking existing
algorithms from commercial applications and find use cases for these in the
military domain. This requires a broader understanding of technology and a
deeper understanding of the entire battle design framework. A silo based
approach would be highly expensive, time consuming and only duplicate
algorithms that are already residing in other domains.
By itself, AI cannot provide a complete solution and the
requisite underlays of hardware and the overlays of networks and systems are a
necessity. The operational knowledge built into AI can create competencies that
can enhance operational capabilities of submarines on sea-beds. Cognitive
frameworks built on AI can help submarines sense qualitative changes in the
environment and help react with more sophisticated options.
 |
| Europian Unmanned ground war vehicle |
An uncrewed vehicle or unmanned vehicle: is a vehicle without a person on board. Uncrewed vehicles can either be under telerobotic control—remote controlled or remote guided vehicles—or they can be autonomously controlled—autonomous vehicles—which are capable of sensing their environment and navigating on their own.
7) use of AI in the
field of Space Exploration:
 |
| Unmanned Space Exploration By ISRO India to Install Satellite into Space for Better weather forcast and many other things with the Help of AI generated system |
Space exploration is one of humankind’s greatest
undertakings, prompted by a curious mind and a trust for knowledge of what lies
beyond. The latest monumental example of our human curiosity and technological
advancements is the safe landing of the NASA rover Perseverance , which
marked the beginning of the ambitious search for past life on Mars.
Perseverance’s task is to gather soil and rock samples to be studied afterwards
for a potential sign of life. Apart from collecting rock samples, the rover
also provided us with new images of the Red Planet and the first-ever recorded
video and audio of Mars.
 |
| Mar`s Exploration |
The Perseverance rover is not alone on Mars. It’s accompanied by the first helicopter sent to another planet – Ingenuity.
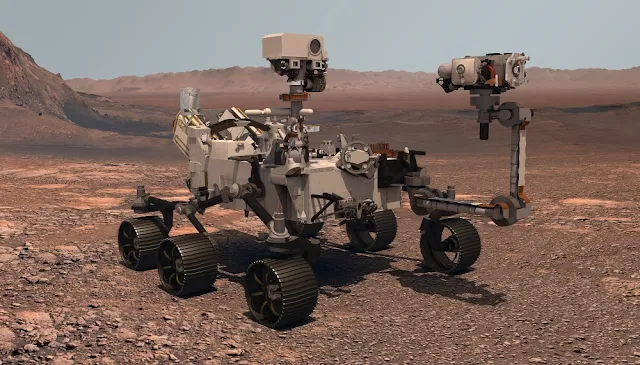 |
| Mar`s Rover |
The 4
pounds (1.8 kilograms) helicopter in the size of a tissue box marks several
other colossal steps in space exploration. Besides being the first aerial
flight on another planet, Ingenuity is the first aircraft to attempt controlled
flight on another planet, which is extremely difficult considering Mars’ thin
atmosphere and bone-chilling conditions. The helicopter is an innovative
experiment, but if it succeeds, it will enable a new aerial dimension of future
Mars exploration with other advanced robotic flying vehicles that could provide
access to terrain that is difficult for rovers to reach or too distant for
orbiters high above. Both Perseverance and Ingenuity use AI throughout their
mission to successfully land, enable engineers to remotely aim and control the
rover’s chemistry camera and navigate autonomously.
All previous or current NASA’s missions in space
exploration have been enabled by AI. We’ve previously touched upon how NASA
uses AI and machine learning for space exploration in the teaser article for
Shreyansh Daftry’s Data Innovation Summit session. In order to appreciate the
great success of NASA and humanity, we are again exploring the current topic,
but with a more in-depth perspective. As an AI Research Scientist at NASA Jet
Propulsion Laboratory, Shreyansh introduced us to the evolution of autonomous
robots for space exploration with AI and ML, challenges and solutions to
training deep learning models in the Martian environment, and lessons and
future AI-powered exploration.
NASA has been building capable spacecraft that have
visited almost all the major object in our Solar System, and exploring new
frontiers in interstellar space for the past 60 years.
However, space exploration in the past didn’t always
include intelligent machines. In fact, the Apollo mission that carried the
first humans to the moon performed a proper landing thanks to Neil Armstrong’s
abilities, who manually piloted the spacecraft. Another example is the
Curiosity rover, which is one of the most capable space machines, but it’s
remotely operated by humans from the mission control room on Earth.
Although man-operated space machines worked in the past,
they are not scalable for future missions. “There is a growing need for future
spacecraft to be autonomous, self-aware and be able to make critical decisions
on their own,” explained Shreyansh. There are two main factors for this. The
first factor is the difficulty with deep space communication and critical
missions, especially involving the outer planets of our solar system. Due to
the large distance and the limited bandwidth of radio signals, the only way the
far-off planets can be explored is by sending fully-autonomous robots. The
second factor is scalability. Future missions will require many more satellites
and space assets that would require 100+ engineers and scientists controlling
them remotely from the Earth. If we want to scale out the space economy, our
space assets need to be self-sustainable. AI is a crucial ingredient in making
both factors a reality.
Shreyansh outlined several key capabilities that would
require AI-powered space exploration for future robotic missions, such as
autonomous navigation, autonomous science and mission operations, scheduling
and planning, precision landing, autonomous manipulation, allowing robots to
perform dexterous operations and future missions with human-robot teams. There
are numerous other AI applications in space exploration beyond robotics and
automation, but they are outside of Shreyansh scope of work. In his talk, he
focused on AI application in autonomous navigation.
Challenges and solutions to training deep learning models
on Martian environment
Thanks to the ongoing developments in computer vision,
deep learning and AI, NASA has made great strides in their space exploration
missions. However, adopting the deep learning models and neural networks to
Martian conditions presents an exponential challenge, or rather a set of
challenges, stated Shreyansh, such as availability of data, severely limited
onboard computation and system validation to gain trust.
To secure data sets for training and transfer learning,
they asked their rover drivers and scientists on the Mars rover mission to
label a small amount of data with high-quality labels. To augment the labelled
data, they launched the AI4Mars citizen science project using free
crowdsourcing from the internet community to label the Curiosity images using a
web-based tool. To overcome the additional challenge of people’s lack of
knowledge and the noise in the labelled data, they developed a workshop-style
tutorial and interactive tool in 10+ languages.
Additionally, they looked into the rapidly developing
area of high-fidelity simulation and generating synthetic data for improving
their deep learning pipelines. Based on this method, they successfully created
the SPOC classifier to segment Mars terrain types.
To tackle the limited computation challenge, they
deployed the SPOC-lite algorithm on a test rover and tested. SPOC-lite can
easily identify sandy surfaces from rock surfaces.
The third challenge of system integration and end-to-end
verification is the most overlooked in the data science and machine learning
community, but it is especially important in highly-complex safety-critical
cyber-physical systems like spacecraft, highlighted Shreyansh. Deep learning
algorithms and neural network models are instrumental in training the rovers,
but they are inherently “black box”, presenting a major obstacle in model
validation and performance. When the rover is launched in space, they can’t fix
things if something goes wrong. As their machine learning system deployment has
to work on the first shot, it requires exhaustive system integration,
validation and testing campaign, which involves creating scenarios that can be
expected on Mars and going crazy with testing.
Future AI-powered
NASA missions:
Sending Perseverance and Ingenuity to Mars was a colossal
achievement for NASA and AI. In future, NASA plans to send similar rovers to
the Moon, Mars and beyond. The next few decades of robotic space exploration
will involve the outer planets and their moons, stated Shreyansh.
To prepare for the planned mission on Jupiter’s moon
Europa, NASA has been developing robots that can learn how to walk, ski, drive
on its icy surface and dive in the oceans to look for evidence of life. The
robots have to be completely autonomous and without any human involvement for
several hours on end. An additional challenge is the unknown subterranean
nature of the environment. “This is one of the greatest challenges for AI and
robotics for the century,” adds Shreyansh.
As for future Mars missions, the next ambition is to
explore the caves and lava tubes that have the highest potential for a human
colony. To build capabilities for navigating the steep slopes, NASA has been
developing the LEMUR robot capable of climbing almost vertical slopes.
Looking forward, one of the most exciting NASA
undertakings would be AI-powered human exploration, where humans and robots
would go on exploratory missions together. So the next milestone for Shreyansh
and his team would be exploring how they can enable human Mars exploration and
the role AI would play in it, especially in the context of human-robot teams.

































 Online Movies
Online Movies
No comments:
Post a Comment