 |
| Human Brain and Neurone |
Human brain:
The human
brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is
larger than any other in relation to body size. Large animals such as whales
and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using the
encephalization quotient which compensates for body size, the human brain is
almost twice as large as the brain of the bottle nose dolphin, and three times
as large as the brain of a chimpanzee. Much of the expansion comes from the
part of the brain called the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes,
which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning,
reasoning, and abstract thought. The portion of the cerebral cortex devoted to
vision is also greatly enlarged in humans.
 |
| The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals |
The human
cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the
brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that
can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across
individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided
into four "lobes", called the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal
lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic
lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous
cortical areas, each associated with a particular function such as vision,
motor control, language, etc. The left and right sides of the cortex are
broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides.
Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are
involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is
"dominant" for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor
role. There are other functions, such as spatiotemporal reasoning, for which
the right hemisphere is usually dominant.
 |
| Different Parts of Neurone |
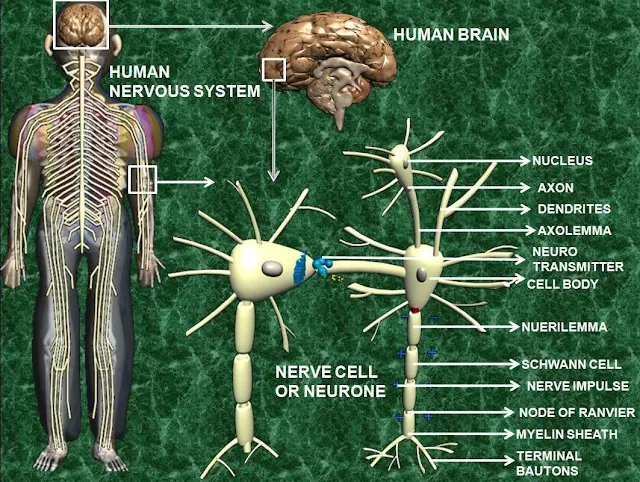
NEURONES:
The
nervous systems consists of vast number of cells called neurones,supported by a
special type of connective tissue ,neuroglia. each neurone consists of a cell
body and its processes,one axon and many dendrites.Neurone are reffered to as
nerve cells.Bundles of axons bound together are called nerves. Neurones cannot
divide,and for survival they need a continuous supply of oxygen and
glucose.Unlike many other cells, neurones can synthesise chemical energy(ATP)
only
from
glucose.The physiological units of nervous system are nerve impulses or action
potential, which are akin to tiny electrical charges.However, Unlike ordinary electrical
wires, the neurones are actively involved in conducting nerve impulses In
effect the initial strength of the impulse is maintained throughout the length
of the neurone.Some neurones initiate nerve impulses are passed on and
sometimes redirected.
PROPERTIES
OF NEURONES:
Irritability
is the ability to initiate nerve impulses in response to stimuli from:
·
Outside the body e.g. touch light waves
·
Inside the body e.g. a change in the
concentration of carbon-di-oxide in the blood alters respiration; a thought
may result in voluntary movement.
CELL
BODIES:
Nerve
cell vary considerably in size and shape but they are all too small to be seen
by the naked eye.Cell bodies from the grey matter of the nervous system and are
found at the periphery of the brain and in the centre of the spinal cord.Groups
of cell bodies are called nuclei in the central nervous system and ganglia in
the peripheral nervous system.An important exception is the basal
ganglia(Nuclei) situated within the cerebrum.
AXONS
AND DENDRITES:
Axons and
dendrites are extensions of cell bodies and from the white matter of the
nervous system.Axons are found deep in the brain and in groups called tracts,at
the periphery of the spinal cord.They are reffered to as nerves or nerve fibres
outside the brain and spinal cord.
Structure
of axons:
The
membrane of the axon is called the axolemma and it encloses the
cytoplasmic extension of the cell body.Large axons and those of peripheral
surrounded by myelin sheath. This consists of a series of schwann cell
arranged along the length of the axon.There are tiny areas of exposed axolemma
between adjacent schwann cells,called nodes of Ranvier,which assist the rapid
transmission of nerve impulses in myelinated neurones. Some small fibres in the
central nervous system are non-myelinated .The speed of transmission of
nerve impulses is significantly slower in non-myelinated fibres.
Dendrites:
This are
the many short processes that receive and carry incoming impulses towards cell
bodies.They have the same structure as axons but are ususally shorter and
branching.In motor neurones they form the part of the synapes and in sensory
neurone they form the sensory receptors that respond to specific stimuli.
 |
| Different parts of Human brain |
CEREBRUM:
This is
the largest part of the brain and its occupies the anterior and middle cranial
fossae.It is divided by a deep cleft,The longitudinal cerebral fissure, into
right and left cerebral hemisphere each containing one of the lateral
ventricles.Deep within the brain.The
hemispheres are connected by a mass of the white matter called the corpus
callosum.The falx cerebri is formed by the dura mater.It separates the 2
hemisphere and penetrates to the depth of the corpus callosum.The superficial
part of the cerebrum is composed of nerve cell bodies or grey matter,forming
the cerebral cortex and the deeper layers consist of nerve fibres or white
matter.
The cerebral cortex shows many
infolding or furrows of varying depth.The exposed areas of the folds are the
gyri or convolutions and these are separated bu sulci.These convolutions
greatly increased the surface area of the cerebrum.For descriptive purposes
each hemisphere of the cerebrum is divided into lobes which take the names of
the bones of the cranium under which they lie:
·
Frontal
·
Parietal
·
Temporal
·
Occipital
The
boundaries of the lobes are marked by deep sulci.These are the central,lateral
and parieto-occipital sulci.
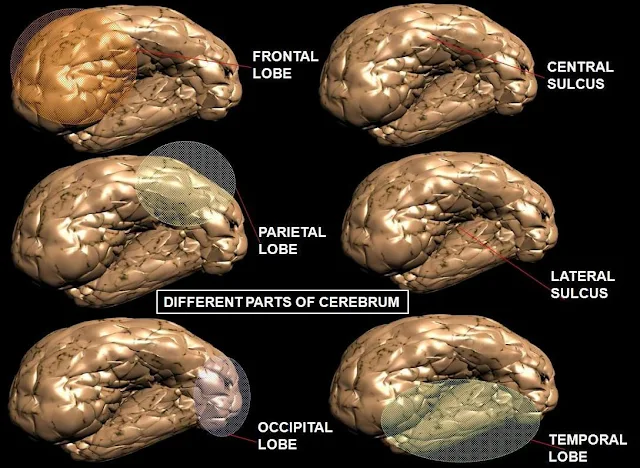 |
| Different Parts of Cerebrum |
 |
| Different Sensory Complex Response Control Area of Cerebrum |
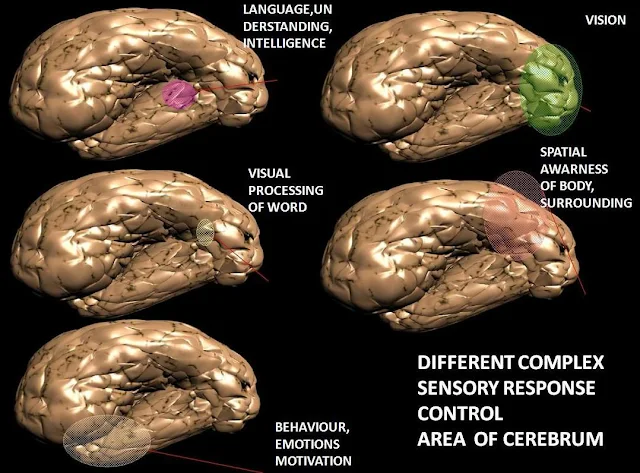 |
| Different Sensory Complex Response Control Area of Cerebrum |
CEREBELLUM:
The
cerebellum is situated behind the pons and immediately below the posterior
cranial fossa.It is ovoid in shape and has two hemispheres, separated by a
narrow median strip aclled vermis. Grey matter forms the surface of the
cerebellum, and the white matter lies deeply.
Functions:
·
It co-ordinates activities associated with
the maintenance of posture,balance and equilibrium.
·
The cerebellum may also have a role in
learning and language processing.
 |
| Different Parts of Meninges |
MENINGES:
The brain
and spinal cord are completely surrounded by three layers of tissue, the
meninges, lying between the skulland the brain, and between the vertebral
foramina and the spinal cord.Named from outside inwards they are the:
·
Dura mater
·
Arachnoid mater
·
Pia mater
The dura
and arachnoid maters are separated by a potential space, the subdural space.The
arachnoid and pia matersare separated by the subarachnoid space ,
containing cerebrospinal fluid.
Dura
mater:
The
cerebral dura mater consists of two layers of dense fibrous tissue. The outer
layer takes the place of the periosteum on the inner surface of the skull bones
and the inner layer provides a protective covering for the brain.There is only
a potential space between the two layers except where the inner layer sweeps
inwards between the cerebral hemispheres to form falx cerebri; between the
cerebellar hemispheres to form the falx cerebelli; and between the cerebrum and
cerebellum to form the tentorium cerebelli. Venous blood from the brain drains
into venous sinuses between the dura mater.
Arachnoid
mater:
This is a
layers of fibrous tissue that lies between the dura and pia maters.It is
separated from the dura mater by the subdural space, and from the pia mater by
the subarachnoid space,containing cerebrospinal fluid.The arachnoid passes
through the convolutions of the brain and accompanies the inner layer of dura
mater in the formation of the falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli and falx
cerebelli.
Pia
mater:
This is
delicate layer of connective tissue containing many minute blood vessels. It
adheres to the brain,completelycovering the convultions and and dipping into
each fissure.It continues downwards surrounding the spinal cord.Beyonds the end
of the cord it continues as the filum terminale,pierces the arachnoid tube and
goes on, with the dura mater, to fuse with the periosteum of the coccyx.
 |
| Different parts of Human brain |
THE
LATERAL VENTRICLES:
These
cavities lie within the cerebral hemispheres,one on each side of the median
plane just below the corpus callosum.They are separated from each other by a
thin membrane ,the septum lucidum and are lined with ciliated epithelium.They
communicate with the 3rd ventricle by interventricular foramina.
THIRD
VENTRICLE:
The 3rd
ventricle is a cavity situated below the lateral ventricles between the two
parts of the thalamus.It communicates with the 4th ventricle by a canal, the cerebral
aqueduct.
THE FOURTH
VENTRICLE:
The 4th
ventricle is a diamond-shaped cavity situated below and behind the 3rd ventricle,between
the cerebellum and pons .It is continuous below with the central canal of the
spinal cord and communicates with the sub arachnoid space by foramina in its
roof.Cerebrospinal fluid enters the sub arachnoid space through these openings
and through the open distal end of the central canal of the spinal cord.
























 Online Movies
Online Movies
ReplyDeleteFurniture Removals Wollongong treat all of our Local Wollongong Moving customers as our biggest customers. We treat each customer the same as we would expect to be treated if we were moving locally, providing a world-class customer care service, taking care of every single item that is to be moved to your new home. Our Furniture Removals Wollongong is dedicated to helping residential movers and commercial movers in Wollongong, providing a professional service that you will be proud to recommend to your family and friends.call 1300 09 09 77 to book.
This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDelete