RENAISSANCE:
From the 15 th century Europe experienced a remarkable flowering of the arts and Sciences. This was known as the " Renaissance" , which is French means " Rebirth". From its Birthplace in Italy, the Renaissance spread to embrace most of western Europe, and deeply affected the way educated people looked at the world and its purpose. Inspired by the study of ancient Greeks and Roman society, Renaissance scholars , thinkers and Artists abandoned medieval pessimism and constructed humanism - new optimistic outlook for the future, in which men and women played a central role and created a civilized environment. Some of the world`s finest art and literature dates from this period.

RENAISSANCE Origins:
The Renaissance Began in Italy when the Poets, Dante, Petratch and Boccaccio revived an interest in ancient Greek and Roman Civilizations. They believed these socities had experienced a Golden Age of art and literature in the 2nd and 1 st centuries BC, and wished to recreate it.
Petrarch:
The poet Petrarch (1304-1374) was a brilliant scholar of Latin. He studied the ancient authors Plato, Virgil and Cicero. The work of these scholars became known as the " Classics" because of the elegance of their writing. Eventually this term included Greek and Roman architecture and art, as well as literature.
New order:
Medieval thinkers argued that earthly life was less important than the afterlife. In contrast, The Renaissance view was that the mortal world, with all its human achievements, was the most significant part of the God`s Creation. This Inspired explorers. inventors, and Astronomers to expand human knowledge.
Age of Exploration:
Fired by the new spirit of enquiry , the Portuguese sailors Bartolomeu Diaz and Vasco da Gama discoverd the sea route to India. Ferdinand Magellan set out to sail around the world, though he did not live to complete the trip.
Stars and Planets:
The astronomer Copernicus was the first to realize that the Universe did not revolve around Earth. Instead Earth revolved around the Sun. Later astronomers, such as Galileo, supported this theory, and went on to form new ones, using the same system of Planetary observation that Copernicus Had Pioneered.

Human Body:
Medieval artists viewed the human form as "a withered fruit stinking in the nostril of the Lord". The Renaissance overturned this view, and artists such as Michelangelo, Raphael, and Titian portrayed the human figure with beauty and grace. Michelangelo`s sculpture the Pieta idealizes the human forms to represent their spiritual purity.
Anatomy:
The body`s structure fascinated Renaissance artists. Leonardo da Vinci advanced human knowledge and enabled artists to represent the body more accurately by realistic sketches of faces, and diagrams of muscle movements.

Michelangelo:
Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475-1594) from Caprese, Tuscany, Italy, was one of the greatest artistic creators of all time. A sculptor, painter, draughtsman, poet and architect, he was deeply fascinated by the human body and its representation. Sculpture was the art from he loved best. When he sculpted, he believed that he was "releasing" the figures trapped in the stone.His greatest painting was on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in the Vatican, Rome.
Albrecht Durer:
From Germany was one of the greatest Renaissance artists. One of 18 children, Durer was apprenticed to a painter and book illustrator at 15 years old. After 4 years Durer began to travel around Europe, and picked up new ideas from other artists, including Bellini and Raphael. A true Renaissance man who mastered many subjects from Latin to mathematics, He is mainly remembered for his exquisite engravings and wood block prints.
Perspective in Painting:
The greatest innovation in Renaissance art was the development of perspective. Artists, keen to represent the natural world accurately, learned how to put space and distance in the their paintings. This had been missing in the flatter, two-dimensional works of the medieval period.

The Catholic Church:
By 1400, the Church had become wealthy, worldly and corrupt. The renaissance directly challenged what was left of curch authority, because it emphasized the importance of enquiry. Churchmen ignored any suggestion of reform as, for the first time, cartoons circulated that made fun of the church and its inability to cope with new ideas.
Humanism:
As the Renaissance spread, northern European scholars developed humanism, a philosophy that greatly valued human dignity and moral values. The first humanists were passionate Christians.They studied the classics (Ancient Latin, Greek, and Hebrew texts) and revolutionized education bt teaching the mumanities (moral philosophy, grammer, history, rhetoric, and poetry) instead of just learning the Bible by heart.
Desiderius Erasmus:
The humanist movement in Europe affected Germany, Holland and England. Erasmus (1468-1536) was a brilliant Dutch humanist, who led the revival of learning. He became famous through his religious translations and writings, in which he gently and humorously called for peaceful reform in the Church.
Sir Thomas More (1477-1535) was a humanist. His book " Utopia" argued that all political and social evils would be cured by the common ownership of land, the education of both women and men, and religious tolerance.
Education:
Humanists felt that people shaped their own destiny, and that Greek and Roman texts illustrated this. Therefore English humanist educators, such as Sir John Cheke (1514 - 1557) and Nicholas Udall (1505-1556), encouraged children to study the classics so they learned how to serve their society for the common good.
Renaissance Princes:
As the Renaissance Progressed, Ruler became more sophisticated and ruthless. The political writer Niccolo Machiavelli (1469 - 1527) described the art of statecraft in his book " The Prince (1532). He formed many of his theories by comparing his own Italian society with that of ancient Rome.

Francis I (1515-1547):
Regarded himself as a perfect Renaissance prince. An able, quick witted man, He loved art and learning and was the patron of geniuses such as Leonardo da Vinci and Benvenuto Cellini (1500-1591). In June 1520 , he vied with the era`s other great Renaissance prince Henry VIII of England , at a magnificent summit meeting at the field of the Cloth of Gold near Calais, France.


The Medici of Florence:
The Medici banking family rose to power in the early Renaissance and contributed much to the flowering of the arts. They made Florence an artistic and cultural centre , all of the great artists went there. Even those who were not patronized by the Medici, such as the Tuscan portraitist Artemisia Gentileschi (1590-1642), went to Florence to make contacts and improve their Skills.

Printing:
Few inventions have had a greater impact on the world than printing. Printing as we know it, from movable metal type, was the invention of a gold-smith of Mainz in Germany , Johannes Gutenberg. Several people were experimenting in the 1440s but it was Gutenberg who brought his process to perfection by about 1454. His Invention consisted of a type-mould for casting the individual letters, a press adapted from the wine-press of the day, and a suitbly sticky ink, The press could print about 300 sheets a day.


Printing enabled books to be produced more quickly, cheaply, and accurately than by hand-coying, so boosting the spread of Knowledge.
From the 15 th century Europe experienced a remarkable flowering of the arts and Sciences. This was known as the " Renaissance" , which is French means " Rebirth". From its Birthplace in Italy, the Renaissance spread to embrace most of western Europe, and deeply affected the way educated people looked at the world and its purpose. Inspired by the study of ancient Greeks and Roman society, Renaissance scholars , thinkers and Artists abandoned medieval pessimism and constructed humanism - new optimistic outlook for the future, in which men and women played a central role and created a civilized environment. Some of the world`s finest art and literature dates from this period.

RENAISSANCE Origins:
The Renaissance Began in Italy when the Poets, Dante, Petratch and Boccaccio revived an interest in ancient Greek and Roman Civilizations. They believed these socities had experienced a Golden Age of art and literature in the 2nd and 1 st centuries BC, and wished to recreate it.
Petrarch:
The poet Petrarch (1304-1374) was a brilliant scholar of Latin. He studied the ancient authors Plato, Virgil and Cicero. The work of these scholars became known as the " Classics" because of the elegance of their writing. Eventually this term included Greek and Roman architecture and art, as well as literature.
 |
| Petrarch |
Medieval thinkers argued that earthly life was less important than the afterlife. In contrast, The Renaissance view was that the mortal world, with all its human achievements, was the most significant part of the God`s Creation. This Inspired explorers. inventors, and Astronomers to expand human knowledge.
Age of Exploration:
Fired by the new spirit of enquiry , the Portuguese sailors Bartolomeu Diaz and Vasco da Gama discoverd the sea route to India. Ferdinand Magellan set out to sail around the world, though he did not live to complete the trip.
 |
| Bartolomeu Diaz |
 |
| Bartolomeu Diaz-Route of his Journey |
 |
| Vasco da Gama |
Stars and Planets:
The astronomer Copernicus was the first to realize that the Universe did not revolve around Earth. Instead Earth revolved around the Sun. Later astronomers, such as Galileo, supported this theory, and went on to form new ones, using the same system of Planetary observation that Copernicus Had Pioneered.
 |
| Copernicus |
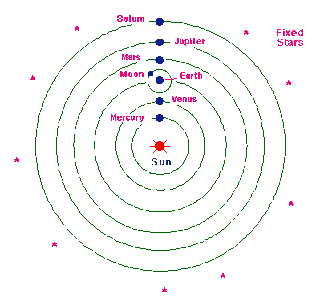 |
| Copernicus`s Universe |

Human Body:
Medieval artists viewed the human form as "a withered fruit stinking in the nostril of the Lord". The Renaissance overturned this view, and artists such as Michelangelo, Raphael, and Titian portrayed the human figure with beauty and grace. Michelangelo`s sculpture the Pieta idealizes the human forms to represent their spiritual purity.
 |
| Michelangelo`s sculpture the Pieta |
The body`s structure fascinated Renaissance artists. Leonardo da Vinci advanced human knowledge and enabled artists to represent the body more accurately by realistic sketches of faces, and diagrams of muscle movements.
 |
| Leonardo da Vinci-Self Portrait |
 |
| Anatomy Pics from Notebook of Leonardo |

Michelangelo:
Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475-1594) from Caprese, Tuscany, Italy, was one of the greatest artistic creators of all time. A sculptor, painter, draughtsman, poet and architect, he was deeply fascinated by the human body and its representation. Sculpture was the art from he loved best. When he sculpted, he believed that he was "releasing" the figures trapped in the stone.His greatest painting was on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in the Vatican, Rome.
 |
| Michelangelo Buonarroti |
 |
| Creation of Adam |
 |
| Ulysses_and_the_Sirens-The_Beauty_the_Truth_the_Virtue |
From Germany was one of the greatest Renaissance artists. One of 18 children, Durer was apprenticed to a painter and book illustrator at 15 years old. After 4 years Durer began to travel around Europe, and picked up new ideas from other artists, including Bellini and Raphael. A true Renaissance man who mastered many subjects from Latin to mathematics, He is mainly remembered for his exquisite engravings and wood block prints.
 |
| Albrecht Durer |
 |
| Virgin and a Child |
 |
| knight-albrecht-durer |
Perspective in Painting:
The greatest innovation in Renaissance art was the development of perspective. Artists, keen to represent the natural world accurately, learned how to put space and distance in the their paintings. This had been missing in the flatter, two-dimensional works of the medieval period.

The Catholic Church:
By 1400, the Church had become wealthy, worldly and corrupt. The renaissance directly challenged what was left of curch authority, because it emphasized the importance of enquiry. Churchmen ignored any suggestion of reform as, for the first time, cartoons circulated that made fun of the church and its inability to cope with new ideas.
Humanism:
As the Renaissance spread, northern European scholars developed humanism, a philosophy that greatly valued human dignity and moral values. The first humanists were passionate Christians.They studied the classics (Ancient Latin, Greek, and Hebrew texts) and revolutionized education bt teaching the mumanities (moral philosophy, grammer, history, rhetoric, and poetry) instead of just learning the Bible by heart.
Desiderius Erasmus:
The humanist movement in Europe affected Germany, Holland and England. Erasmus (1468-1536) was a brilliant Dutch humanist, who led the revival of learning. He became famous through his religious translations and writings, in which he gently and humorously called for peaceful reform in the Church.
 |
| Desiderius Erasmus |
 |
| Sir Thomas More |
 |
| Book Written by Sir Thomas More |
Education:
Humanists felt that people shaped their own destiny, and that Greek and Roman texts illustrated this. Therefore English humanist educators, such as Sir John Cheke (1514 - 1557) and Nicholas Udall (1505-1556), encouraged children to study the classics so they learned how to serve their society for the common good.
Renaissance Princes:
As the Renaissance Progressed, Ruler became more sophisticated and ruthless. The political writer Niccolo Machiavelli (1469 - 1527) described the art of statecraft in his book " The Prince (1532). He formed many of his theories by comparing his own Italian society with that of ancient Rome.

Francis I (1515-1547):
Regarded himself as a perfect Renaissance prince. An able, quick witted man, He loved art and learning and was the patron of geniuses such as Leonardo da Vinci and Benvenuto Cellini (1500-1591). In June 1520 , he vied with the era`s other great Renaissance prince Henry VIII of England , at a magnificent summit meeting at the field of the Cloth of Gold near Calais, France.


The Medici of Florence:
The Medici banking family rose to power in the early Renaissance and contributed much to the flowering of the arts. They made Florence an artistic and cultural centre , all of the great artists went there. Even those who were not patronized by the Medici, such as the Tuscan portraitist Artemisia Gentileschi (1590-1642), went to Florence to make contacts and improve their Skills.

Printing:
Few inventions have had a greater impact on the world than printing. Printing as we know it, from movable metal type, was the invention of a gold-smith of Mainz in Germany , Johannes Gutenberg. Several people were experimenting in the 1440s but it was Gutenberg who brought his process to perfection by about 1454. His Invention consisted of a type-mould for casting the individual letters, a press adapted from the wine-press of the day, and a suitbly sticky ink, The press could print about 300 sheets a day.


Printing enabled books to be produced more quickly, cheaply, and accurately than by hand-coying, so boosting the spread of Knowledge.
























 Online Movies
Online Movies
No comments:
Post a Comment