RECOMBINANT
DNA TECHNOLOGY (CLONING):
You might
say that recombinant DNA technology grew out of experiments with E.coli and the
bacteriophages that infect
it. In
the late 1960s and early 1970s, researches learned how to use a variety of
cutting and splicing enzymes to make
DNA
fragments and "package" them in plasmids for insertion into host
cells.They developed ways to pinpoint the DNA fragments of interest in
individual lines lines of dividing cells.They also started to identify the
nucleotide sequences of individual genes and to sequence the genome.For
different spaecies. The following eaxamples will give you a sense of what the
new technology entails.
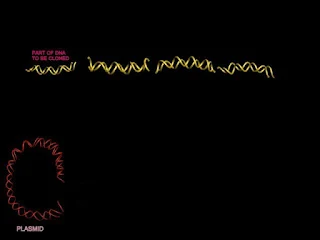
1) Restriction enzymes cuts
chromosomal DNA at specific recognition sites.
2) Same restriction enzymes is used
to cut plasmids.
3) Cut plasmid DNA and fragments of
chromosomal DNA are joined using DNA ligase.
4) Recombinant plasmids containing cloned
library. So we now have plasmids into which DNA fragments are spliced for
propagation in host cells. A plasmid or
any other self-replicating genetic element used to insert DNA into a host cell
or propagation is called a cloning
vector.Any collection of DNA fragments produced by restriction enzymes and
incor
- porated
into cloning vectors is called a DNA library.Each library contains DNA
fragments from a single species only.





























 Online Movies
Online Movies
No comments:
Post a Comment